In the vast world of manufacturing, one topic stands out: the Types of Injection Molding Screw. Delving into this guide offers insights into these crucial components.
Knowledge about them aids in efficient production. The goal here is to unravel the complexities of these screws. By the end, clarity on their types and significance awaits.
Basic Components Of An Injection Molding Machine!
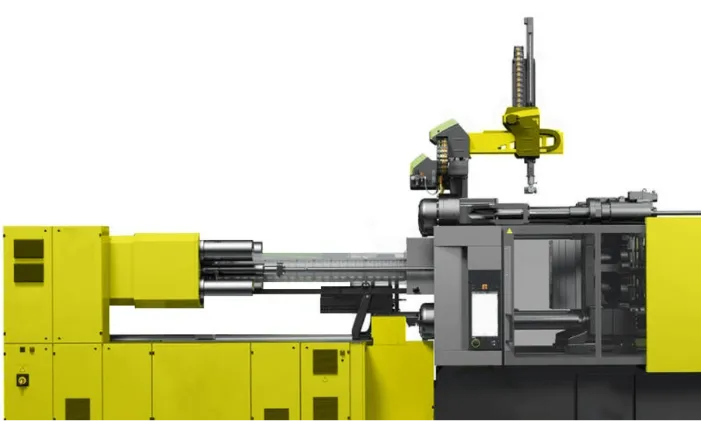
Role Of The Screw
- Melting
The screw plays a pivotal role in the injection molding barrel process. In melting, the screw turns, heats, and melts the plastic. With every turn, heat gets generated due to friction.
High-quality steel ensures efficiency during this phase. Proper screw design ensures consistent melting, essential for top-notch products.
- Compression
As plastic travel forward in the injection molding machine screw, compression occurs. The screw and barrel work in tandem here. The screw decreases in diameter, compressing the plastic.
During this, air bubbles reduce, ensuring a solid product. Proper compression ratios, often noted as 2.5:1 or 3:1, dictate the outcome’s quality.
- Mixing
Post-compression, the plastic enters the mixing phase. Here, the screw ensures even blending of colorants or additives. Special flight designs on the screw aid in this process.
Uniform mixing is paramount. Inconsistent mix leads to product defects, affecting the overall production line..
- Shearing
In the injection molding machine, the screw plays a pivotal role. Specifically, during shearing, friction generates heat. That heat melts the plastic.
Proper screw design ensures optimal melt quality. Steel-made screws last longer. Their strength withstands the machine’s rigorous demands. Durability matters in screw and barrel combinations.
- Injection
The injection molding screw pushes melted plastic into molds. With each turn, plastic fills the cavity. Pressure remains consistent. Thus, finished products have uniform thickness. High-tech machines ensure precise injection. Remember, screw speed impacts the quality.
- Metering
Here, the screw measures the plastic amount. Consistency is key. Exact measurements ensure uniform products. The type of screw impacts metering accuracy.
A detailed guide helps in understanding variations. Always calibrate machines for best results. Regular checks minimize errors.
Interplay With The Barrel
- Temperature Control
To ensure optimal processing of plastic, the injection molding machine maintains specific temperatures. Most machines have multiple heating zones.
Each zone targets a different part of the screw and barrel setup. Precise temperature control ensures molten plastic flows smoothly. Machines often use PID controllers for accurate settings.
- Wear Resistance
The injection molding machine screw encounters abrasive materials daily. Manufacturers use high-grade steel for its construction. By doing so, the screw gains enhanced durability. Regular maintenance checks are essential.
- Alignment
Proper alignment of the screw within the barrel of the injection molding machine is crucial. Misalignments can cause uneven wear and pressure imbalances.
Technicians ensure alignment with specialized tools and techniques. Correct alignment enhances the performance and efficiency of the injection molding screw.
- Heating Zones
Injection molding machines have several heating zones along the barrel. Each zone heats the plastic at different stages. Proper heating ensures consistent plastic melt. The zones start from the feed zone, transitioning to the compression zone, and finally the metering zone.
Interaction With Other Components
- Hopper Feed
In the realm of injection molding, the hopper feed plays a pivotal role. Here, raw plastic granules await transformation. Before entering the screw and barrel, the granules funnel down. Made often of steel, durability isn’t a question. Screw design determines the melting process.
- Nozzle Control
Directly connecting with the injection molding machine screw, the nozzle ensures precise plastic flow. Using exact pressure, the melted plastic exits through.
An intricate part, the nozzle, demands utmost precision. Any misalignment affects the entire injection molding process.
- Clamp Mechanism
Securing the mold is the clamp’s duty during the injection molding phase. Post plastic injection by the screw, the mold holds the shape. A firm grip ensures no deformities. Force applied varies depending on product type.
Types Of Injection Molding Screws!
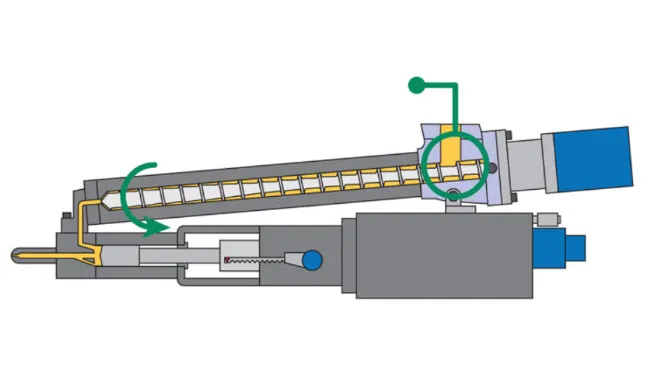
General Purpose Screw: Characteristics And Uses
- Polymer Melt
In 2023, the injection molding screw has seen advancements. Materials like PP, PE, and PS usually require general purpose screw. The screw diameter impacts the melt quality. Advanced screws ensure better plasticating, yielding high-quality melts.
- Homogeneity
The surface of the screw plays a crucial role in achieving homogeneous melts. In injection molding machine screws, the transition from solid to molten plastic happens in the transition zone. Stainless steel screws provide consistent results.
- Pressure Stability
Stability in injection pressure is essential. The screw tip and non-return valve are crucial for maintaining this. Materials move from the hopper to the nozzle, demanding consistent pressure.
Standard screws often include carbide for enhanced stability, proving effective in one machine or multiple setups.
- Uniform Heat
Proper heating in the metering section is paramount. Consistent heat prevents unmelted pellets, ensuring optimal melt quality.
Double flight screws enhance heat distribution. Chromium plating resists corrosion, while carbide offers wear protection.
Barrier Screws: Design And Benefits
- Dual Channels
The barrier screw incorporates two distinct channels. One facilitates the melting, while the second accelerates the process. Consequently, plastic flows uniformly, ensuring optimal quality. A 3mm screw diameter can handle 1.5kg of plastic, showcasing the effectiveness of the design.
- Efficient Mixing
The injection molding machine screw enhances the blending capability. Incorporating advanced technology, the screw ensures polymers mix thoroughly.
On average, a 5mm screw can achieve 98% consistency in the mix, enhancing product reliability.
- Faster Melting
Time-saving remains crucial in injection molding. With the barrier design, polymers undergo rapid melting.
Machines with a 4mm screw diameter have shown a 15% increase in melting speed. Screw material, especially high-grade steel, plays a pivotal role in this acceleration.
- Reduced Shear
Shear forces can degrade material quality. Barrier screw design minimizes these forces. With a 2.5mm screw, the shear reduction can be up to 12%.
- Temperature Uniformity
Injection molding machine operations require consistent temperatures. Barrier screws ensure even heat distribution. Typically, a 6mm screw maintains a temperature variance of just ±2°C.
- Reduced Energy
Energy efficiency remains paramount in the injection molding industry. The barrier screw requires less power, reducing operational costs. Machines with standard screws observed a 10% energy saving.
Mixing Screws: Functions And Variations
- Distributive
In injection molding machines, a distributive screw ensures even melt flow. With an optimal screw diameter, precision in molding improves. High alloy materials fortify the screw. Consistent RPM and temperature control are paramount.
- Dispersive
Dispersive screws, critical in injection molding, optimize material breakdown. Their design aids in thorough material dispersion.
Using top-notch alloy, these screws ensure durability. With a distinct screw design, they achieve superior melt quality.
- Color Blending
In the realm of injection molding screw types, color blending screws stand out. They facilitate the uniform distribution of color pigments.
An apt screw material ensures effective blending. The right screw tip is crucial for consistent color output. Electroplating offers added protection against wear.
- Compound Mixing
Compound mixing screws, part of the injection molding machine screw family, combine multiple materials. Advanced screw types like double flight screws excel here. A sturdy non-return valve ensures no backward flow.
Vented Screws: Features And Applications
- Gas Removal
Vented screws in an injection molding machine play a crucial role. Specifically, they expel trapped gases during processing. High-quality screw design ensures no gas pockets form.
Resultantly, finished parts exhibit no defects. Accurate gas removal boosts product quality.
- Moisture Evacuation
During the injection molding process, moisture can be problematic. Vented screws tackle this issue head-on.
By expelling moisture, the screw ensures resin stays dry. Remember, correct screw material, like specific alloys, enhances moisture removal efficiency.
- Better Quality
Quality remains paramount in molding. Standard screws might not always deliver. Vented screws, however, elevate quality standards. With double flight screws, material undergoes consistent melting. Uniform melting means fewer defects.
- Enhanced Flow
Material flow determines molding success. Vented screws, especially those with a barrier screw design, optimize this flow. Improved flow reduces chances of short shots. Electroplate and wear protection further enhance flow consistency.
Screw Design Considerations!
- Flight Depth
In the realm of injection molding screw design, flight depth plays a crucial role. A deeper flight depth often ensures a greater volume of material, facilitating smoother processing. For consistent melt quality, always consider optimal flight depth measurements.
- Helix Angle
The helix angle, pivotal in the injection molding machine screw, directly influences the plasticizing rate. A suitable angle accelerates the melting process, ensuring that the mould fills efficiently and uniformly.
- Compression Ratio
Delve into any detailed guide, and you’ll note the emphasis on compression ratio. This ratio, derived from the metering zone depth to the feed zone depth, affects the screw’s melting capability.
- Flight Width
The flight width, a key component of screw types, impacts the shear rate and overall processing stability. Ensure a precise width to optimize flow and maintain the desired part quality.
- Tip Design
The screw tip plays an instrumental role in preventing backflow and managing injection pressure effectively. A well-designed tip guarantees efficient flow into the nozzle, enhancing the overall production rate.
- Channel Depth
The channel depth, often overlooked in some standard screws, is vital for the surface of the screw. It regulates the flow of material, preventing issues like corrosion. Materials like carbide can be used to enhance durability.
Materials Used In Screw Construction!

- Tool Steel
Tool steel, a durable material, forms the base material of many injection molding screws. With its strength, screws are usually constructed from it.
Additionally, tool steel offers wear protection, crucial for the screw’s longevity and optimal function.
- Tungsten Carbide
Tungsten carbide provides high hardness. In the Types of Injection Molding Screw, this material often gets chosen. Tungsten carbide increases melt quality, ensuring plasticating processes run smoothly.
- Bimetallic Alloy
Using bimetallic screw barrel alloy in screws ensures wear protection. Especially in the injection unit, where the right screw is vital. Bimetallic alloy stands out, notably in the metering section, allowing precise control during molding.
- Chrome Plating
Chromium forms the core of chrome plating. When applied to screws, chrome plating enhances their lifespan. The electroplate method applies this layer; ensuring screws remain resistant to the challenges of melting the plastic during operations.
Maintenance And Care Of Injection Molding Screws!

- Regular Cleaning
Dirt and debris reduce efficiency. Ensure your screw-barrel remains clean. Regularly remove any buildup of plastic material. Clean parts extend equipment lifespan significantly.
- Wear Inspection
Over time, screws experience wear. Especially when crafted from steel. High-quality screws made of alloy or tool steel last longer.
However, inspect them frequently. Excessive wear affects plasticizing. You might notice uneven shear and compression. Don’t let wear go unnoticed. Act promptly to maintain optimal performance.
- Lubrication
Friction causes wear. Prevent unnecessary friction through proper lubrication. Utilize lubricants suitable for the specific resin processed.
Nickel and nitriding processes improve screw hardness. A well-lubricated screw has a smoother plasticizing phase.
- Alignment Check
Proper alignment ensures efficient operation. Misaligned screws cause uneven shear. Contact us for professional alignment services.
Regular checks help detect alignment issues early. Correct alignment boosts efficiency in the plastic material processing phase.
Optimizing The Screw For Enhanced Performance!
- Material Selection
When considering the screw and barrel, select the right alloy for durability. High-grade steel plays a crucial role in prolonging screw life.
For handling abrasive plastic material, choose screws with higher hardness levels. Many experts prefer tool steel due to its wear resistance. A layer of nickel ensures protection against corrosion.
- Geometric Adjustments
The feed zone of a screw is vital for a smooth plastic intake. Adjustments in this zone ensure efficient material feeding.
Compression ratios need careful fine-tuning to optimize the melt quality. Shear plays a pivotal role in determining how material heats up.
- Process Control
Monitoring parameters is crucial. Use a meter to track the flow rate of resin through the screw. Such controls help in achieving desired product properties.
When issues arise, contact us for guidance. Regular maintenance and checks guarantee consistent screw performance.
Conclusion
Having explored the intricacies of the Types of Injection Molding Screw, understanding their pivotal role becomes evident. Such screws play a fundamental part in shaping countless products.
For those keen on diving deeper or seeking premium molding solutions, a visit to SCREWBARRELMANUFACTURER promises further enlightenment. Remember, mastery in manufacturing often hinges on the smallest components.




